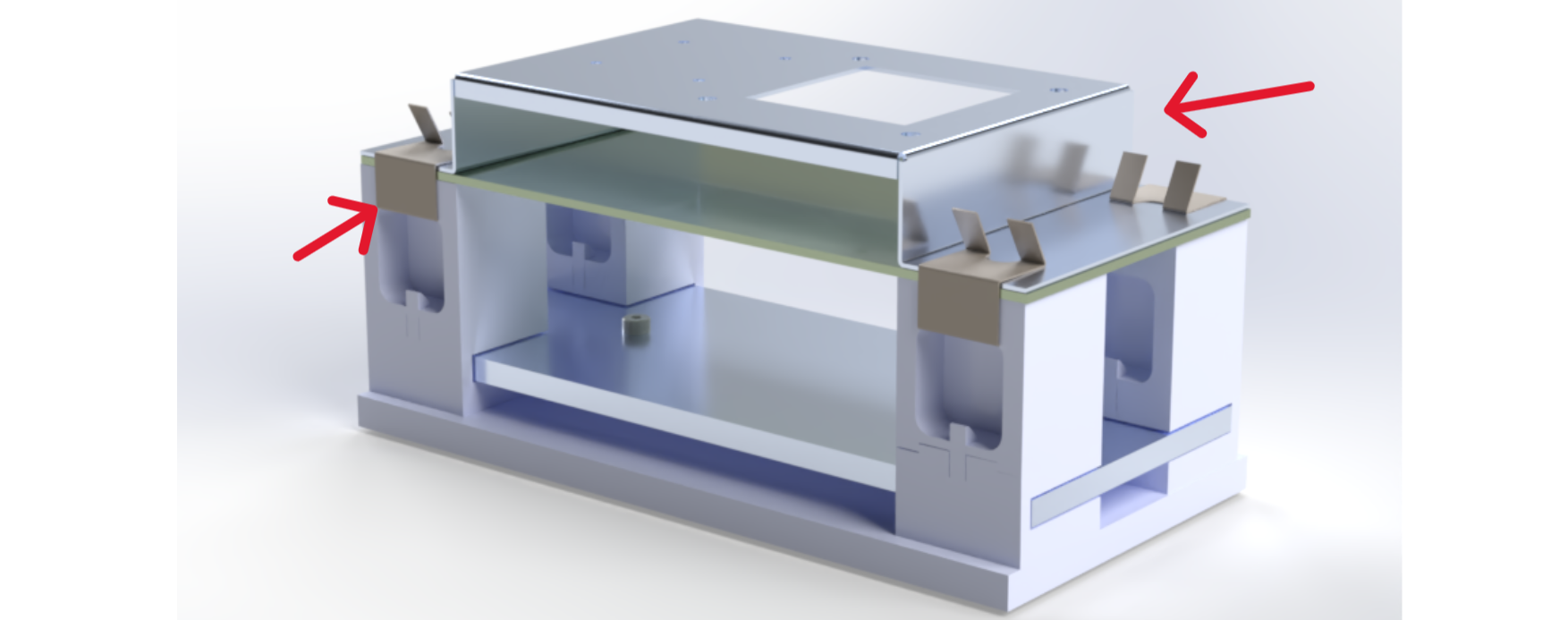
System Context
The sheet-metal components were developed as part of a multi-component PCB mounting assembly with tight geometric and assembly constraints. The parts directly interfaced with machined and additively manufactured components, making tolerance stack-up and assembly order critical. Design decisions were made with continuous coordination across upstream and downstream teams to maintain alignment and functional fit.
Design & Iteration
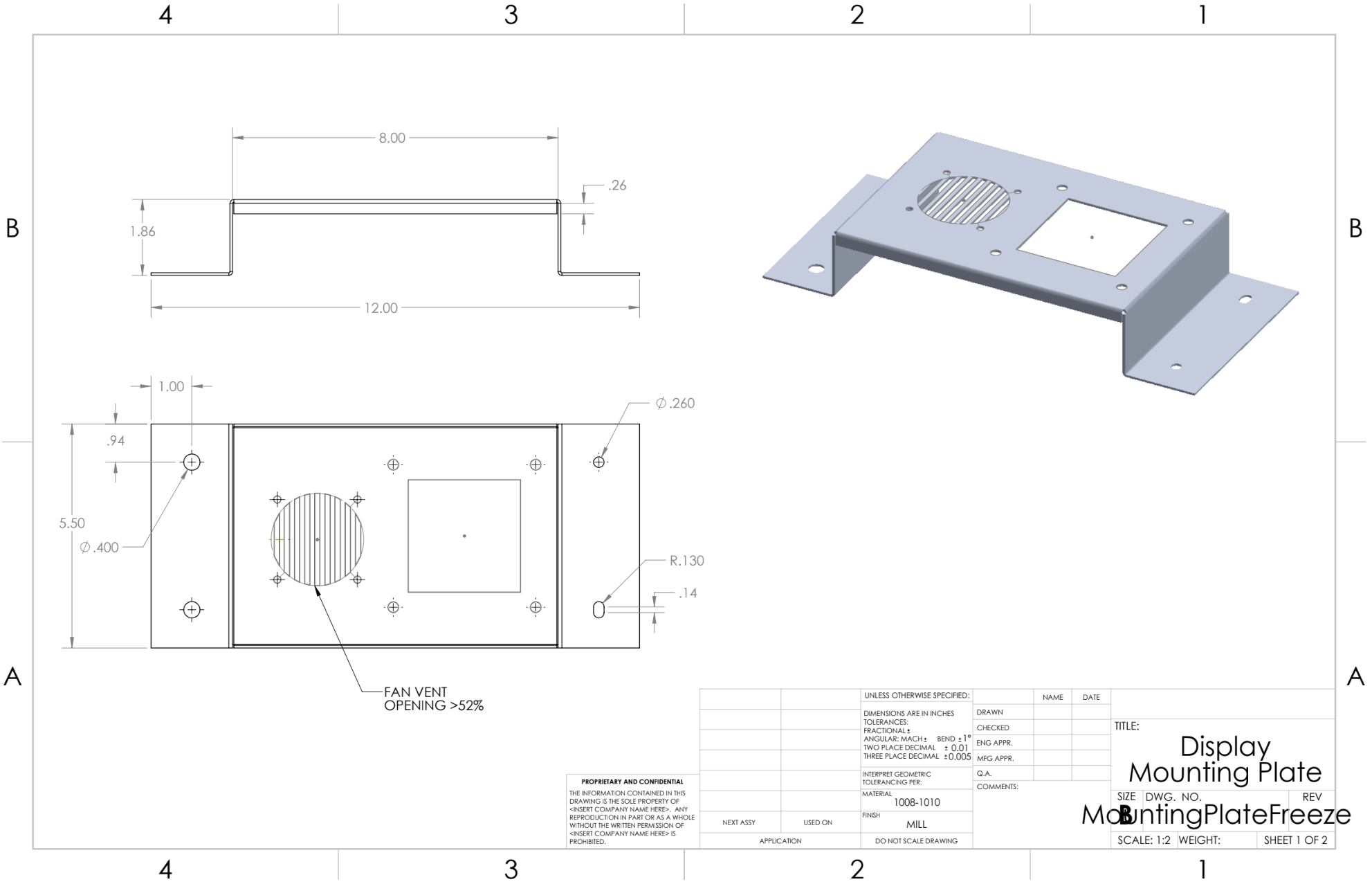
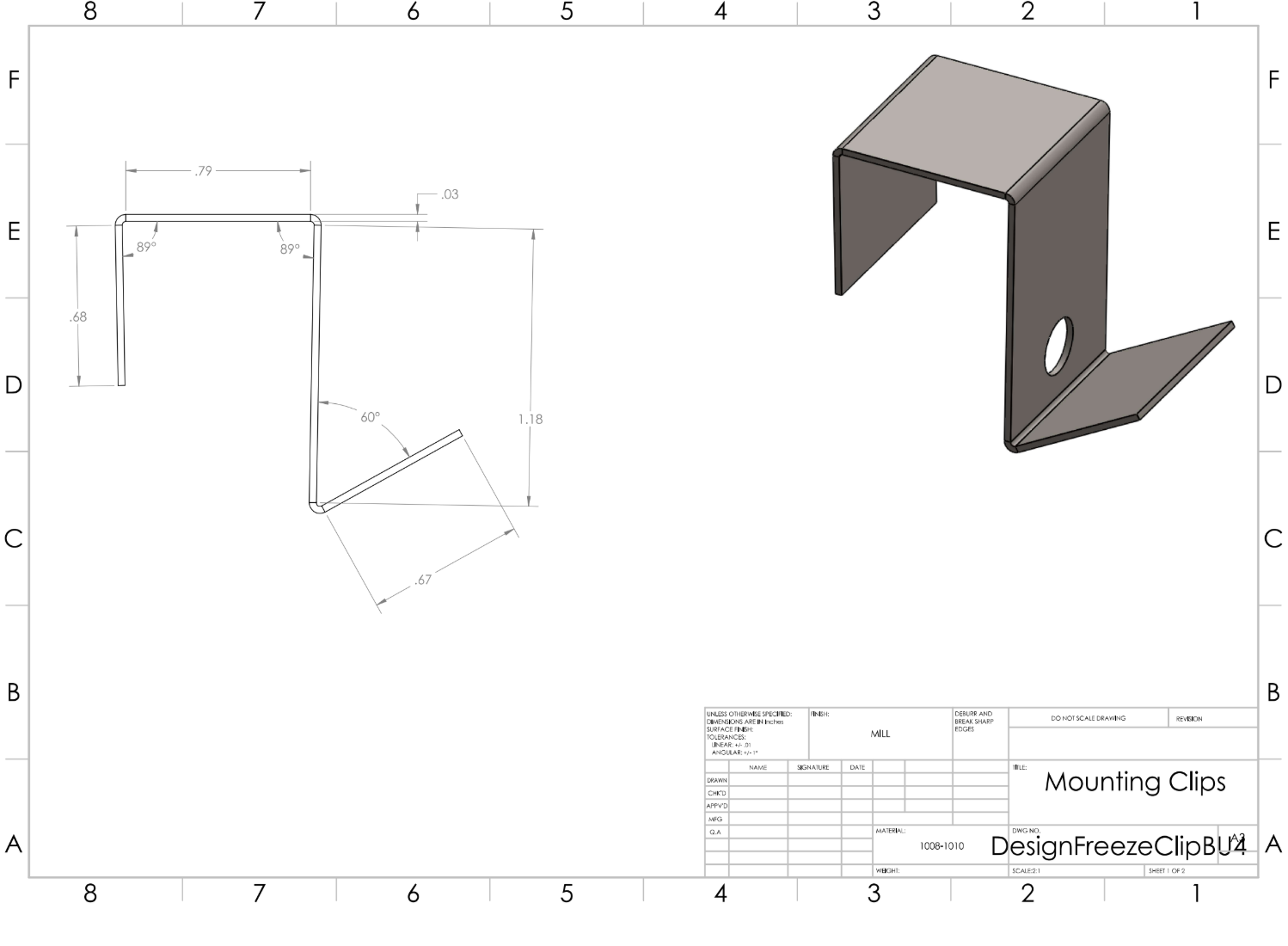
The mounting clips and display mounting plate were designed in SolidWorks and iterated through multiple DFMA reviews. Geometry was refined to remain manufacturable using water-jet cutting and manual forming while preserving functional requirements. Oversized and slotted features were intentionally used to reduce sensitivity to bend-angle variation and improve assembly robustness.
IMAGE HERE – CAD drawings or close-up renders of the clips and mounting plate
Prototyping & Manufacturing
Flat patterns were water-jet cut, deburred, and manually formed using a sheet-metal brake. Bend sequencing and over-bending were adjusted during prototyping to compensate for springback. First-article parts were physically fabricated and modified based on fit and inspection feedback.
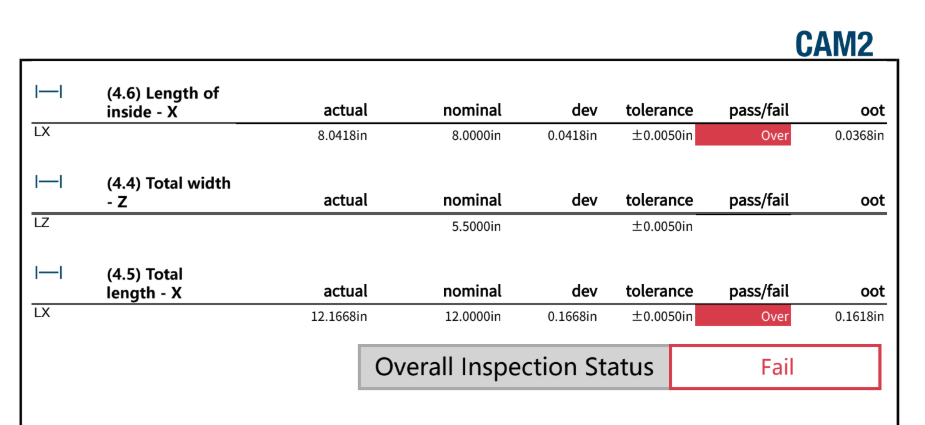
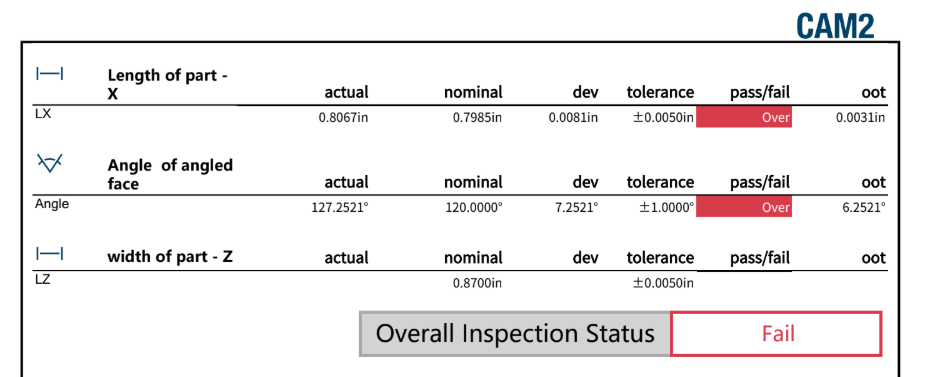
Inspection & Findings
Inspection results showed consistent dimensional drift driven by manual bending variability, particularly in bend angle, which compounded across multiple features. While parts assembled successfully, the data confirmed that the manual forming process was not capable of meeting tight dimensional tolerances at scale.
Assembly & Production Insight
Despite dimensional variation, the components met functional assembly requirements and integrated reliably within the system. The results highlighted the gap between functional success and dimensional compliance, reinforcing the need to align design expectations with true process capability.


Engineering Takeaway
This project reinforced that manufacturability and process capability must drive design decisions. Manual sheet-metal forming introduces repeatability limits that require either automated processes or design compensation strategies to achieve scalable production.
