Simulation Overview
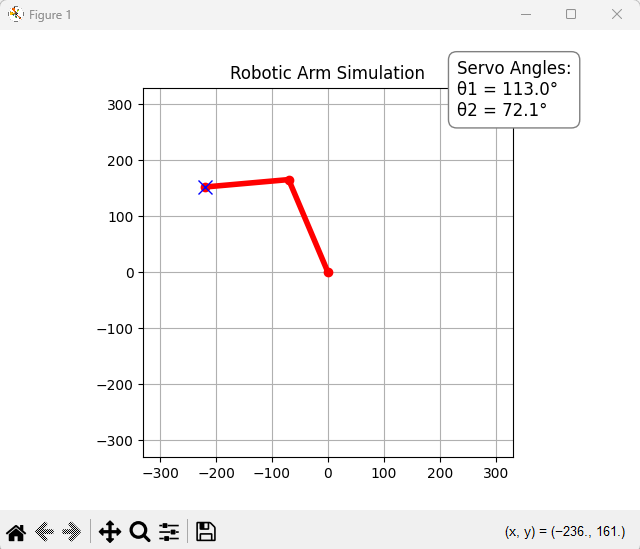
Code for Simulation
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Arm segment lengths
L1 = 180 # 18 cm
L2 = 150 # 15 cm
# Servo angle limit: ±160° in radians
ANGLE_LIMIT = 8 * np.pi / 9 # ~2.79 radians
# Create the figure
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlim(-L1 - L2, L1 + L2) # normal axis range
ax.set_ylim(-L1 - L2, L1 + L2)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.grid(True)
plt.title("Robotic Arm Simulation")
# Initialize plot elements
arm_line, = ax.plot([], [], 'ro-', linewidth=4)
target_dot, = ax.plot([], [], 'bx', markersize=10)
# Place the angle box neatly in upper-right area (inside plot, out of the way)
angle_text = ax.text(
L1 + L2 - 100, L1 + L2 - 50, '', fontsize=12, color='black',
bbox=dict(facecolor='white', edgecolor='gray', boxstyle='round,pad=0.5')
)
def inverse_kinematics(x, y):
D = np.hypot(x, y)
if D > (L1 + L2):
x *= (L1 + L2) / D
y *= (L1 + L2) / D
D = L1 + L2
cos_theta2 = (x**2 + y**2 - L1**2 - L2**2) / (2 * L1 * L2)
cos_theta2 = np.clip(cos_theta2, -1.0, 1.0)
theta2_options = [np.arccos(cos_theta2), -np.arccos(cos_theta2)]
for theta2 in theta2_options:
k1 = L1 + L2 * np.cos(theta2)
k2 = L2 * np.sin(theta2)
theta1 = np.arctan2(y, x) - np.arctan2(k2, k1)
y1 = L1 * np.sin(theta1)
if y1 >= 0 and abs(theta1) <= ANGLE_LIMIT and abs(theta2) <= ANGLE_LIMIT:
return theta1, theta2
return None, None
def forward_kinematics(theta1, theta2):
x0, y0 = 0, 0
x1 = L1 * np.cos(theta1)
y1 = L1 * np.sin(theta1)
x2 = x1 + L2 * np.cos(theta1 + theta2)
y2 = y1 + L2 * np.sin(theta1 + theta2)
return [(x0, y0), (x1, y1), (x2, y2)]
def on_mouse_move(event):
if event.xdata is None or event.ydata is None:
return
x, y = event.xdata, event.ydata
theta1, theta2 = inverse_kinematics(x, y)
if theta1 is None:
return
joints = forward_kinematics(theta1, theta2)
xs, ys = zip(*joints)
arm_line.set_data(xs, ys)
target_dot.set_data([x], [y])
# Update servo angle display
angle_text.set_text(
f"Servo Angles:\nθ1 = {np.degrees(theta1):.1f}°\nθ2 = {np.degrees(theta2):.1f}°"
)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('motion_notify_event', on_mouse_move)
plt.show()

